20 Resources That'll Make You More Efficient At German As A Foreign La…
페이지 정보

본문
Learning German as a Foreign Language: A Comprehensive Guide
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to communicate in multiple languages is more important than ever. Among European languages, German stick out not only for its frequency in academic and professional spheres but likewise for its cultural richness and historic significance. This article explores the fundamentals of finding out German as a foreign language, offering insights into its linguistic structure, advantages, resources, and common challenges dealt with by learners.
The Importance of Learning German
German is the most widely spoken native language in the European Union, with around 90 million speakers worldwide. As the official language of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, it acts as a bridge for global company, cultural exchange, and travel. Here are some factors why discovering German can be beneficial:
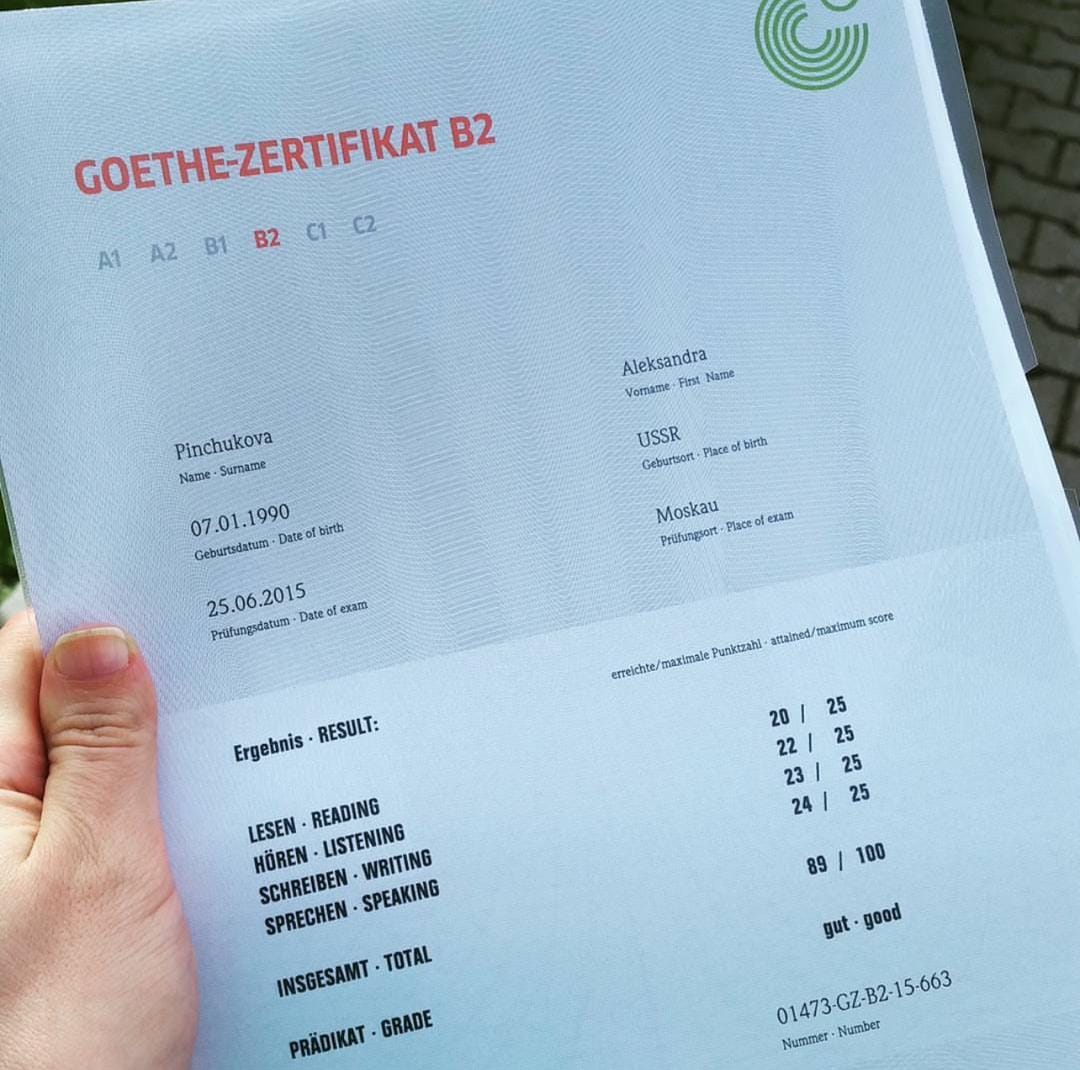 Economic Opportunities: Germany boasts the biggest economy in Europe and the fourth biggest worldwide. Proficiency in German can improve job prospects, especially in industries such as engineering, innovation, and finance.
Economic Opportunities: Germany boasts the biggest economy in Europe and the fourth biggest worldwide. Proficiency in German can improve job prospects, especially in industries such as engineering, innovation, and finance.
Cultural Insights: Germany has a rich cultural heritage, home to popular figures in philosophy, literature, music, deutschprüfung and art. Discovering the language opens doors to comprehending works by Goethe, Nietzsche, Bach, and many others in their original type.
Educational Benefits: Germany provides various scholarship chances for global trainees, frequently needing proficiency in German. Knowledge of the language can supply access to premium education in prominent universities.
Personal Growth: Mastering a new language is a rewarding challenge that enhances cognitive skills, such as problem-solving, imagination, and memory.
Comprehending German Linguistics
German is a West Germanic language that shares roots with English and Dutch. It features a special syntax and ÖSD-Zertifikat C2 grammatical structure that can be challenging for students accustomed to simpler languages. Here are key components of German linguistics:
Noun Genders: Unlike English, German nouns are categorized into three genders: manly (der), feminine (die), and neuter (das). This classification impacts article usage and adjective endings.
Cases: German uses four grammatical cases-- nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Each case affects noun and short article forms, suggesting the noun's function in a sentence (subject, item, and so on).
Compound Words: German is known for its compound nouns, where numerous words combine to develop a single term. For example, "Handschuh" (hand DeutschprüFung shoe) means "glove.".
Effective Strategies for Learning German.
Knowing German requires a thoughtful technique that integrates various techniques to cater to individual learning designs. Here are some reliable strategies:.
1. Enroll in Language Courses.
Think about registering in local language schools or universities offering German as a foreign language. Professional trainers can guide students through structured curricula.
2. Use Online Resources.
Usage platforms such as Duolingo, Babbel, or Rosetta Stone that offer interactive lessons customized to varying ability levels.
3. Experiment Native Speakers.
Engage in conversation with native German speakers through language exchange programs or platforms like Tandem and HelloTalk.
4. Immerse Yourself in Media.
Consume German media, such as films, ÖSD-Zertifikat B2 podcasts, and books. Enjoying German films or series with subtitles can enhance listening understanding and vocabulary.
5. Join Language Communities.
Take part in local or online German-speaking groups. Engaging with others strengthens learning and provides opportunities to practice speaking.
6. Set Realistic Goals.
Establish achievable goals, such as learning a specific variety of brand-new words weekly or practicing promoting a set period every day. Incremental achievements build confidence.
Common Challenges and Solutions.
While discovering German can be satisfying, it also provides numerous obstacles. Here are typical obstacles students face, along with services:.
1. Complex Grammar Rules.
Solution: Regular practice and repeating. Use grammar exercises and resources that breakdown rules in an easily absorbable format.
2. Pronunciation.
Option: Listen to native speakers and mimic their pronunciation. Recording oneself can help identify areas for enhancement.
3. Vocabulary Retention.
Service: Incorporate flashcards (such as Anki) into study regimens to boost memory retention utilizing spaced repeating strategies.
4. Absence of Conversation Practice.
Solution: ÖSD-Zertifikat C1 Set a schedule for weekly conversations with language partners or tutors. This will assist get rid of the fear of speaking and develop fluency.
Frequently Asked Questions About Learning German.
Q1: How long does it require to learn German?
The time it takes to learn German differs based on individual motivation, anticipation of languages, and practice frequency. Usually, students can anticipate to reach conversational fluency in 6 months to 2 years of consistent research study.
Q2: Is German difficult to learn?
German can be challenging due to its grammatical intricacy, however with the right resources and commitment, students can get rid of these challenges. Numerous find it much easier after mastering other Germanic languages such as English or Dutch.
Q3: What resources are recommended for beginners?
For beginners, resources such as Duolingo, Babbel, and language podcasts like "Coffee Break German" are exceptional beginning points. In addition, introductory books can be beneficial for structured learning.
Q4: Do I need to travel to Germany to become fluent?
While immersion can substantially boost language acquisition, it is not necessary to take a trip to Germany. Remote engagement with native speakers and dedicated study can yield considerable progress.
Q5: Can I discover German independently?
Yes, numerous learners effectively teach themselves German through online courses, textbooks, and practice with language partners. Self-directed knowing requires discipline and routine practice.
Conclusion.
Learning German as a foreign language is a gratifying journey that opens many opportunities in expert and personal spheres. By understanding the intricacies of the language and making use of numerous learning techniques, anybody can make significant strides towards fluency. With commitment and practice, the difficulties will gradually fade, causing a newly found gratitude for the appeal and intricacy of this abundant language. Whether for career improvement, cultural gratitude, deutschprüfung or personal growth, Sprachzertifikat b1 mastering German is a valuable possession in today's international landscape, leading the way for deeper connections and understanding.
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to communicate in multiple languages is more important than ever. Among European languages, German stick out not only for its frequency in academic and professional spheres but likewise for its cultural richness and historic significance. This article explores the fundamentals of finding out German as a foreign language, offering insights into its linguistic structure, advantages, resources, and common challenges dealt with by learners.
The Importance of Learning German
German is the most widely spoken native language in the European Union, with around 90 million speakers worldwide. As the official language of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, it acts as a bridge for global company, cultural exchange, and travel. Here are some factors why discovering German can be beneficial:
 Economic Opportunities: Germany boasts the biggest economy in Europe and the fourth biggest worldwide. Proficiency in German can improve job prospects, especially in industries such as engineering, innovation, and finance.
Economic Opportunities: Germany boasts the biggest economy in Europe and the fourth biggest worldwide. Proficiency in German can improve job prospects, especially in industries such as engineering, innovation, and finance.Cultural Insights: Germany has a rich cultural heritage, home to popular figures in philosophy, literature, music, deutschprüfung and art. Discovering the language opens doors to comprehending works by Goethe, Nietzsche, Bach, and many others in their original type.
Educational Benefits: Germany provides various scholarship chances for global trainees, frequently needing proficiency in German. Knowledge of the language can supply access to premium education in prominent universities.
Personal Growth: Mastering a new language is a rewarding challenge that enhances cognitive skills, such as problem-solving, imagination, and memory.
Comprehending German Linguistics
German is a West Germanic language that shares roots with English and Dutch. It features a special syntax and ÖSD-Zertifikat C2 grammatical structure that can be challenging for students accustomed to simpler languages. Here are key components of German linguistics:
Noun Genders: Unlike English, German nouns are categorized into three genders: manly (der), feminine (die), and neuter (das). This classification impacts article usage and adjective endings.
Cases: German uses four grammatical cases-- nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Each case affects noun and short article forms, suggesting the noun's function in a sentence (subject, item, and so on).
Compound Words: German is known for its compound nouns, where numerous words combine to develop a single term. For example, "Handschuh" (hand DeutschprüFung shoe) means "glove.".
Effective Strategies for Learning German.
Knowing German requires a thoughtful technique that integrates various techniques to cater to individual learning designs. Here are some reliable strategies:.
1. Enroll in Language Courses.
Think about registering in local language schools or universities offering German as a foreign language. Professional trainers can guide students through structured curricula.
2. Use Online Resources.
Usage platforms such as Duolingo, Babbel, or Rosetta Stone that offer interactive lessons customized to varying ability levels.
3. Experiment Native Speakers.
Engage in conversation with native German speakers through language exchange programs or platforms like Tandem and HelloTalk.
4. Immerse Yourself in Media.
Consume German media, such as films, ÖSD-Zertifikat B2 podcasts, and books. Enjoying German films or series with subtitles can enhance listening understanding and vocabulary.
5. Join Language Communities.
Take part in local or online German-speaking groups. Engaging with others strengthens learning and provides opportunities to practice speaking.
6. Set Realistic Goals.
Establish achievable goals, such as learning a specific variety of brand-new words weekly or practicing promoting a set period every day. Incremental achievements build confidence.
Common Challenges and Solutions.
While discovering German can be satisfying, it also provides numerous obstacles. Here are typical obstacles students face, along with services:.
1. Complex Grammar Rules.
Solution: Regular practice and repeating. Use grammar exercises and resources that breakdown rules in an easily absorbable format.
2. Pronunciation.
Option: Listen to native speakers and mimic their pronunciation. Recording oneself can help identify areas for enhancement.
3. Vocabulary Retention.
Service: Incorporate flashcards (such as Anki) into study regimens to boost memory retention utilizing spaced repeating strategies.
4. Absence of Conversation Practice.
Solution: ÖSD-Zertifikat C1 Set a schedule for weekly conversations with language partners or tutors. This will assist get rid of the fear of speaking and develop fluency.
Frequently Asked Questions About Learning German.
Q1: How long does it require to learn German?
The time it takes to learn German differs based on individual motivation, anticipation of languages, and practice frequency. Usually, students can anticipate to reach conversational fluency in 6 months to 2 years of consistent research study.
Q2: Is German difficult to learn?
German can be challenging due to its grammatical intricacy, however with the right resources and commitment, students can get rid of these challenges. Numerous find it much easier after mastering other Germanic languages such as English or Dutch.
Q3: What resources are recommended for beginners?
For beginners, resources such as Duolingo, Babbel, and language podcasts like "Coffee Break German" are exceptional beginning points. In addition, introductory books can be beneficial for structured learning.
Q4: Do I need to travel to Germany to become fluent?
While immersion can substantially boost language acquisition, it is not necessary to take a trip to Germany. Remote engagement with native speakers and dedicated study can yield considerable progress.
Q5: Can I discover German independently?
Yes, numerous learners effectively teach themselves German through online courses, textbooks, and practice with language partners. Self-directed knowing requires discipline and routine practice.
Conclusion.
Learning German as a foreign language is a gratifying journey that opens many opportunities in expert and personal spheres. By understanding the intricacies of the language and making use of numerous learning techniques, anybody can make significant strides towards fluency. With commitment and practice, the difficulties will gradually fade, causing a newly found gratitude for the appeal and intricacy of this abundant language. Whether for career improvement, cultural gratitude, deutschprüfung or personal growth, Sprachzertifikat b1 mastering German is a valuable possession in today's international landscape, leading the way for deeper connections and understanding.
- 이전글10 Things That Your Family Taught You About Power Tool Shops Near Me 25.02.19
- 다음글Guide To Mini Exercise Cycle: The Intermediate Guide For Mini Exercise Cycle 25.02.19
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.





